Java & Jenkins Installation
Table of contents
Ubuntu
Installation of Java
sudo apt update
sudo apt install openjdk-11-jre
java -version
openjdk version "11.0.12" 2021-07-20
OpenJDK Runtime Environment (build 11.0.12+7-post-Debian-2)
OpenJDK 64-Bit Server VM (build 11.0.12+7-post-Debian-2, mixed mode, sharing)
curl -fsSL https://pkg.jenkins.io/debian-stable/jenkins.io-2023.key | sudo tee \
/usr/share/keyrings/jenkins-keyring.asc > /dev/null
echo deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/jenkins-keyring.asc] \
https://pkg.jenkins.io/debian-stable binary/ | sudo tee \
/etc/apt/sources.list.d/jenkins.list > /dev/null
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install jenkins
Start Jenkins
You can enable the Jenkins service to start at boot with the command:
sudo systemctl enable jenkins
You can start the Jenkins service with the command:
sudo systemctl start jenkins
You can check the status of the Jenkins service using the command:
sudo systemctl status jenkins
Unlocking Jenkins
When you first access a new Jenkins instance, you are asked to unlock it using an automatically-generated password.
Browse to
http://localhost:8080(or whichever port you configured for Jenkins when installing it) and wait until the Unlock Jenkins page appears.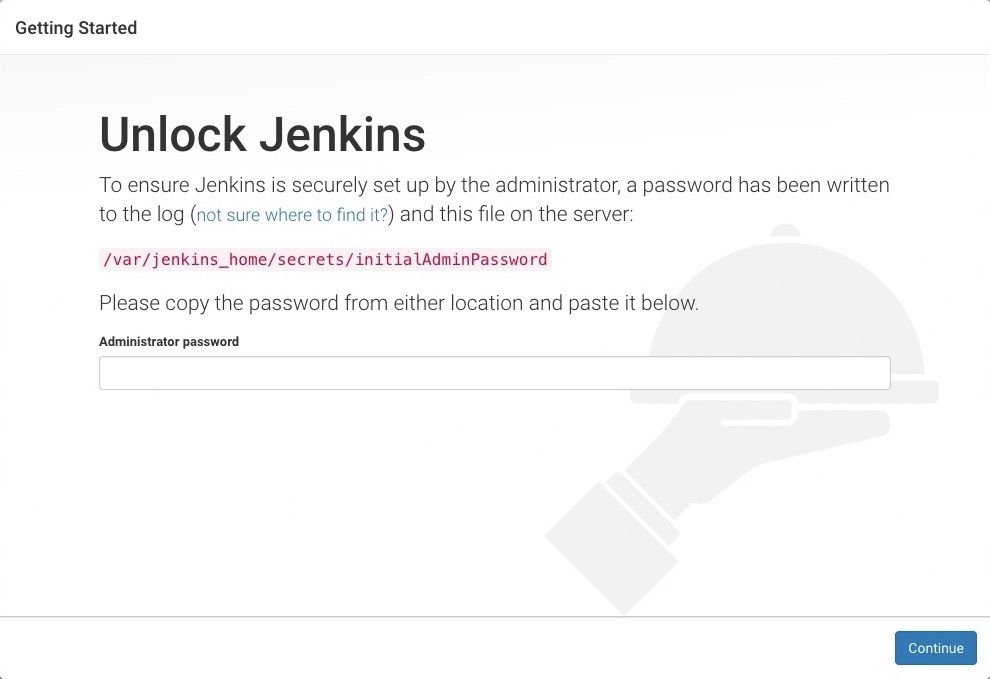
From the Jenkins console log output, copy the automatically-generated alphanumeric password (between the 2 sets of asterisks).
Note:
- The command:
sudo cat /var/lib/jenkins/secrets/initialAdminPasswordwill print the password at console.
- The command:
Installing Docker Compose
Check the current release and if necessary, update it in the command below:
sudo curl -L https://github.com/docker/compose/releases/download/1.29.2/docker-compose-`uname -s`-`uname -m` -o /usr/local/bin/docker-compose
Next set the permissions:
sudo chmod +x /usr/local/bin/docker-compose
Then you’ll verify that the installation was successful by checking the version:
docker-compose --version
This will print out the version you installed:
Outputdocker-compose version 1.29.2, build 5becea4c
Running a Container with Docker Compose
First, you’ll create a directory for the YAML file and move into it:
mkdir hello-world
cd hello-world
Then, you’ll create the YAML file:
nano docker-compose.yml
Put the following contents into the file, save the file, and exit the text editor:
docker-compose.yml
my-test:
image: hello-world
The first line in the YAML file is used as part of the container name. The second line specifies which image to use to create the container. When you run the command docker-compose up it will look for a local image by the name you specified, hello-world. With this in place, you’ll save and exit the file.
You can look manually at images on your system with the docker images command:
docker images
Copy
When there are no local images at all, only the column headings display:
OutputREPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE
Now, while still in the ~/hello-world directory, you’ll execute the following command:
docker-compose up
Windows
Installation steps using Windows MSI installer
Note: Before that please Install Java:11
Step 1: Setup wizard
On opening the Windows Installer, an Installation Setup Wizard appears, Click Next on the Setup Wizard to start your installation.
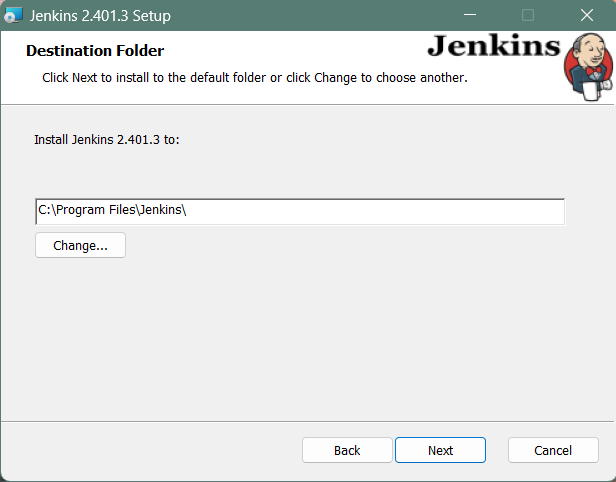
Step 2: Select destination folder
Select the destination folder to store your Jenkins Installation and click Next to continue.
Step 3: Service logon credentials
When Installing Jenkins, it is recommended to install and run Jenkins as an independent windows service using a local or domain user as it is much safer than running Jenkins using LocalSystem(Windows equivalent of root) which will grant Jenkins full access to your machine and services.
To run Jenkins service using a local or domain user, specify the domain user name and password with which you want to run Jenkins, click on Test Credentials to test your domain credentials and click on Next.

If you get Invalid Logon Error pop-up while trying to test your credentials, follow the steps explained here to resolve it. |
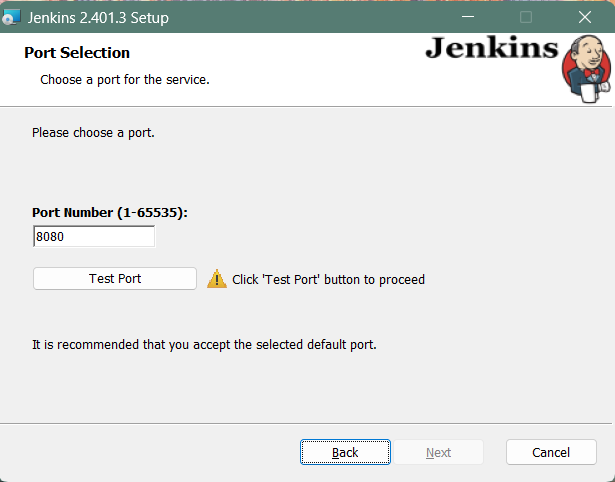
Step 4: Port selection
Specify the port on which Jenkins will be running, Test Port button to validate whether the specified port if free on your machine or not. Consequently, if the port is free, it will show a green tick mark as shown below, then click on Next.
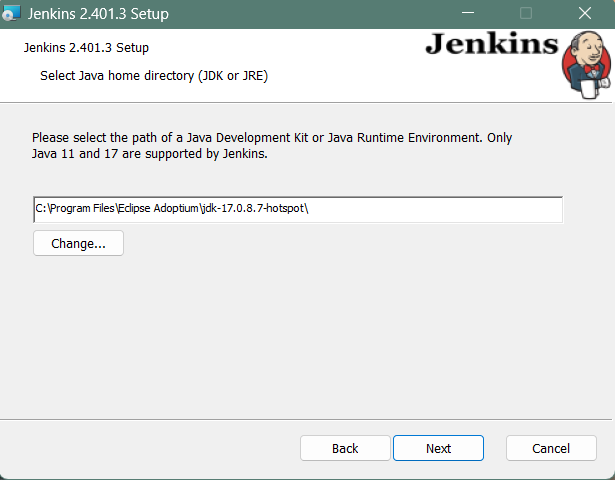
Step 5: Select Java home directory
The installation process checks for Java on your machine and prefills the dialog with the Java home directory. If the needed Java version is not installed on your machine, you will be prompted to install it.
Once your Java home directory has been selected, click on Next to continue.
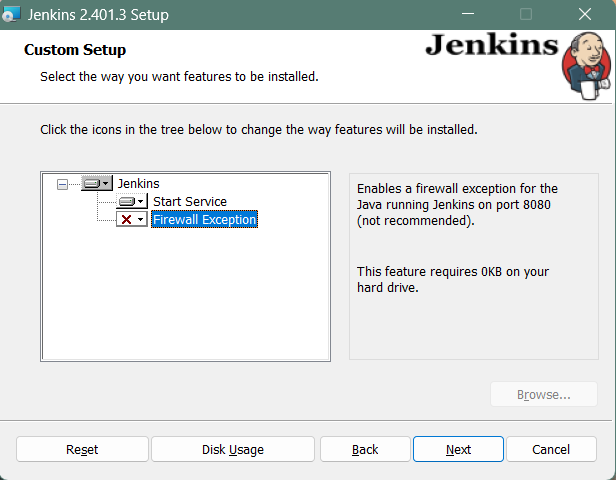
Step 6: Custom setup
Select other services that need to be installed with Jenkins and click on Next.
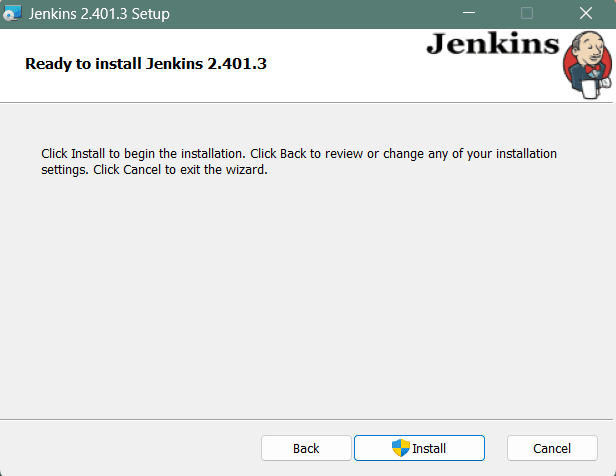
Step 7: Install Jenkins
Click on the Install button to start the installation of Jenkins.
Additionally, clicking on the Install button will show the progress bar of installation, as shown below:
Step 8: Finish Jenkins installation
Once the installation completes, click on Finish to complete the installation.
Jenkins will be installed as a Windows Service. You can validate this by browsing the services section, as shown below:
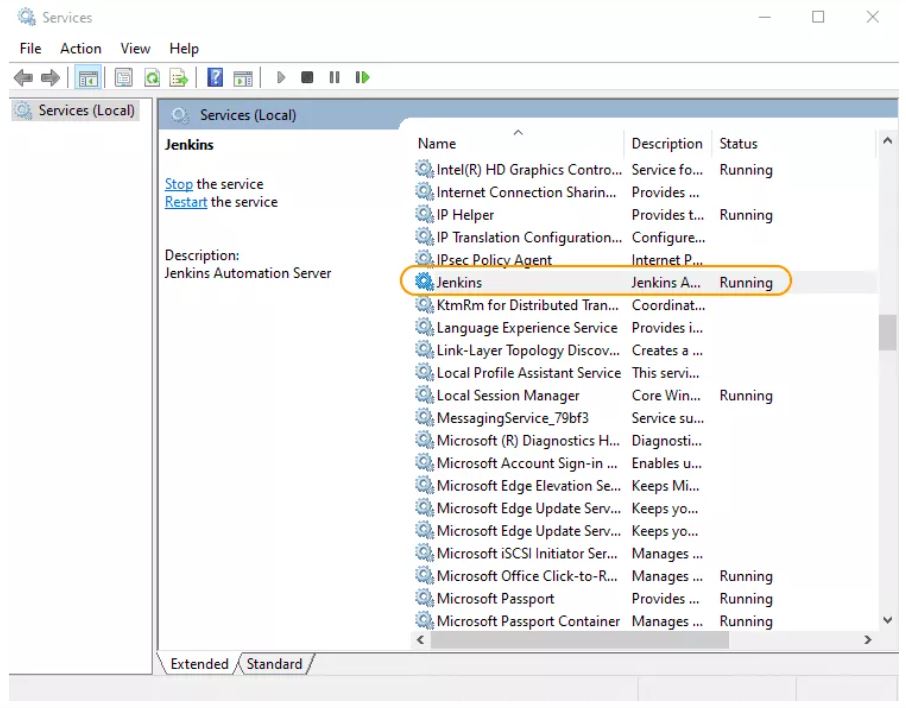
See the upgrade steps when you upgrade to a new release. |
Silent Install with the MSI installers
MSI installers can be installed via a silent method, which can show basic UI (/qb) or no UI at all (/qn). The silent method does not prompt for user input so there are properties that you can pass to the installer to set the specific values. A very basic command line is shown below for a silent install.
msiexec.exe /i "path\to\jenkins.msi" /qn /norestart
This will use all of the default values for things that would normally be a prompt such as:
Installation directory
Service account username/password
Java installation directory
The port for Jenkins to listen on
Each of these things can be overridden by passing a NAME=VALUE property pair for what you want to override:
| Property Name | Description |
| INSTALLDIR | Path to the directory to install Jenkins. (Default: C:\Program Files\Jenkins) |
| PORT | The port Jenkins will listen on. (Default: 8080) |
| JAVA_HOME | The directory where java.exe can be found. (Default: The first Java runtime found in the registry with Java 11 being higher priority than Java 17) |
| SERVICE_USERNAME | The username that the service should run as. The account must have LogonAsService permissions. (Default: In silent mode, the LOCALSYSTEM account) |
| SERVICE_PASSWORD | The password for the SERVICE_USERNAME account. This should only be provided if SERVICE_USERNAME is provided. (Default: In silent mode, none for LOCALSYSTEM) |
A more complex example, including the creation of a log file for the installation process is shown below:
msiexec.exe /i "path\to\jenkins.msi" /qn /norestart INSTALLDIR="D:\Jenkins" JAVA_HOME="C:\Program Files\SomeJava" PORT=80 /L*v "path\to\logfile.txt"
This would install Jenkins into D:\Jenkins, use the Java runtime from C:\Program Files\SomeJava and Jenkins would be listening on port 80.
Post-installation setup wizard
After downloading, installing and running Jenkins, the post-installation setup wizard begins.
This setup wizard takes you through a few quick "one-off" steps to unlock Jenkins, customize it with plugins and create the first administrator user through which you can continue accessing Jenkins.
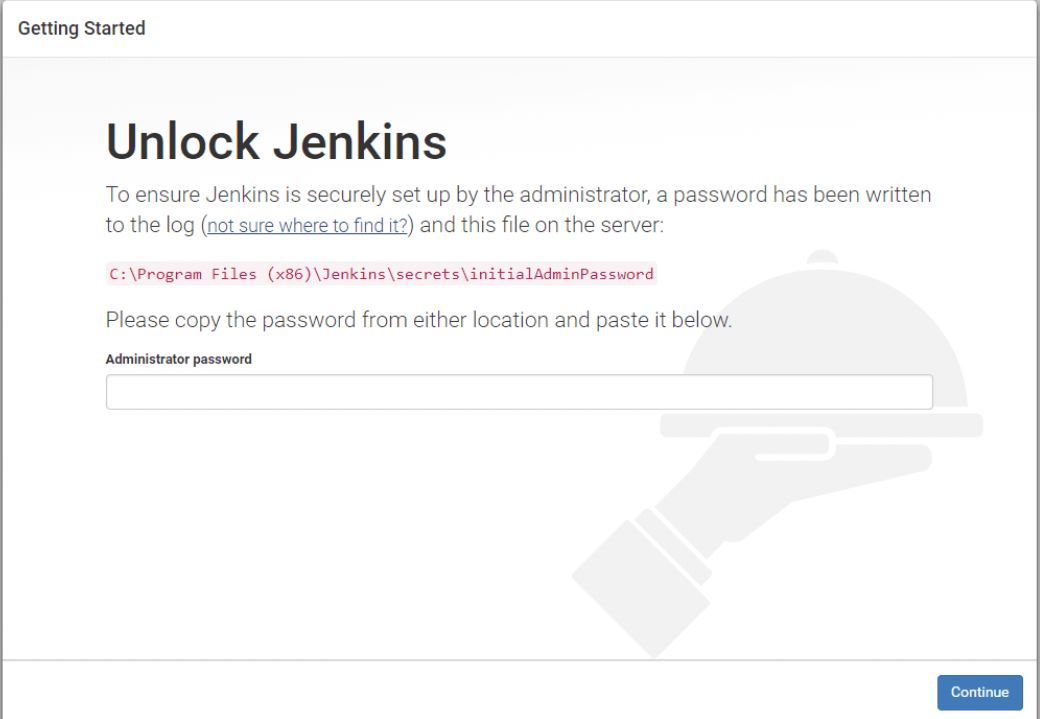
Unlocking Jenkins
When you first access a new Jenkins instance, you are asked to unlock it using an automatically-generated password.
Step 1
Browse to http://localhost:8080 (or whichever port you configured for Jenkins when installing it) and wait until the Unlock Jenkins page appears.
Step 2
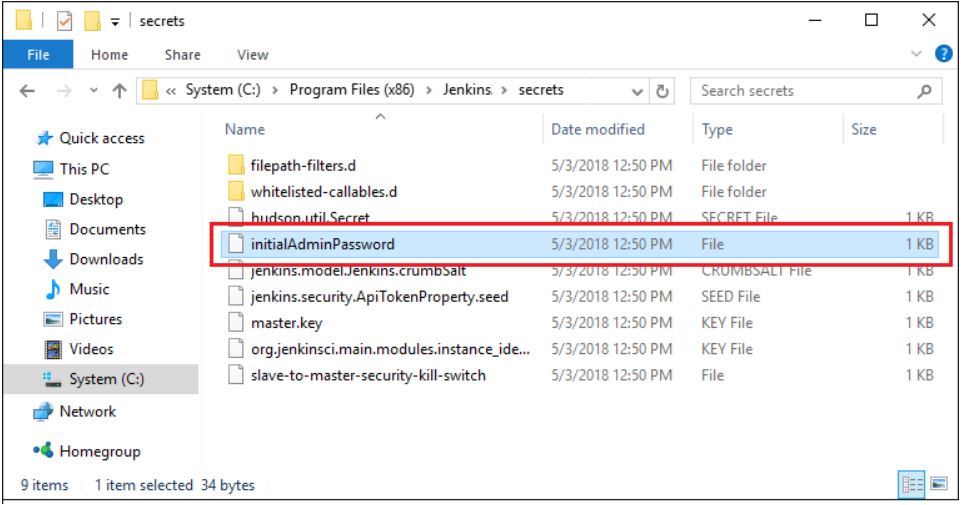
The initial Administrator password should be found under the Jenkins installation path (set at Step 2 in Jenkins Installation).
For default installation location to C:\Program Files\Jenkins, a file called initialAdminPassword can be found under C:\Program Files\Jenkins\secrets.
However, If a custom path for Jenkins installation was selected, then you should check that location for initialAdminPassword file.
Step 3
Open the highlighted file and copy the content of the initialAdminPassword file.

Step 4
On the Unlock Jenkins page, paste this password into the Administrator password field and click Continue.
Notes:
You can also access Jenkins logs in the jenkins.err.log file in your Jenkins directory specified during the installation.
The Jenkins log file is another location (in the Jenkins home directory) where the initial password can also be obtained.
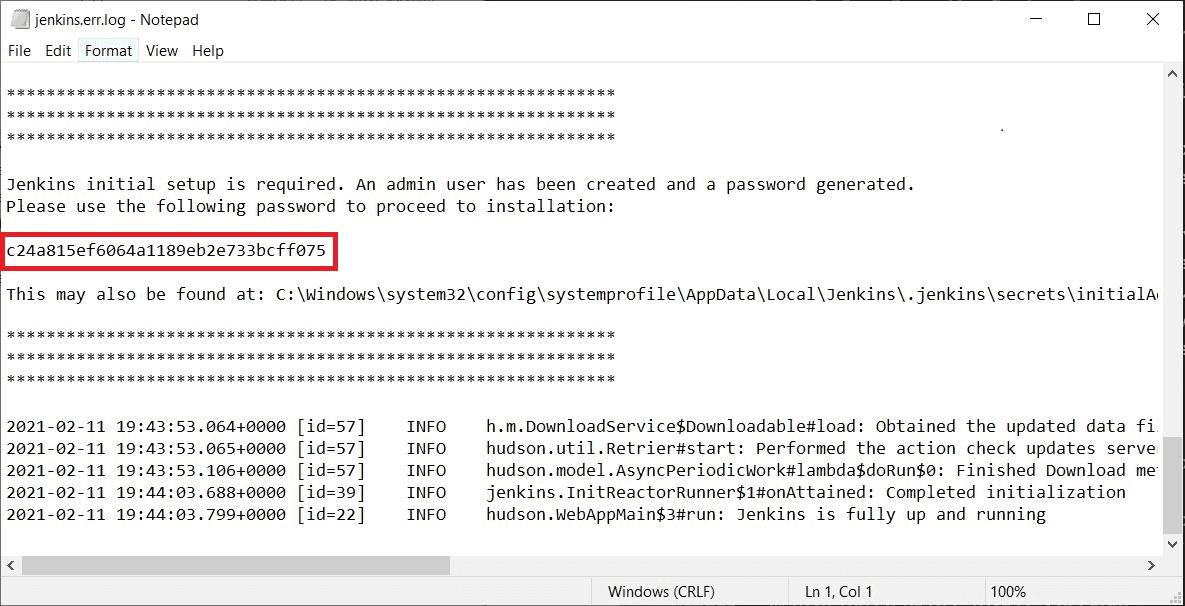
This password must be entered in the setup wizard on new Jenkins installations before you can access Jenkins’s main UI. This password also serves as the default administrator account’s password (with username "admin") if you happen to skip the subsequent user-creation step in the setup wizard.