OCI Compute Service : cheatsheet
OCI Compute Services
Compute
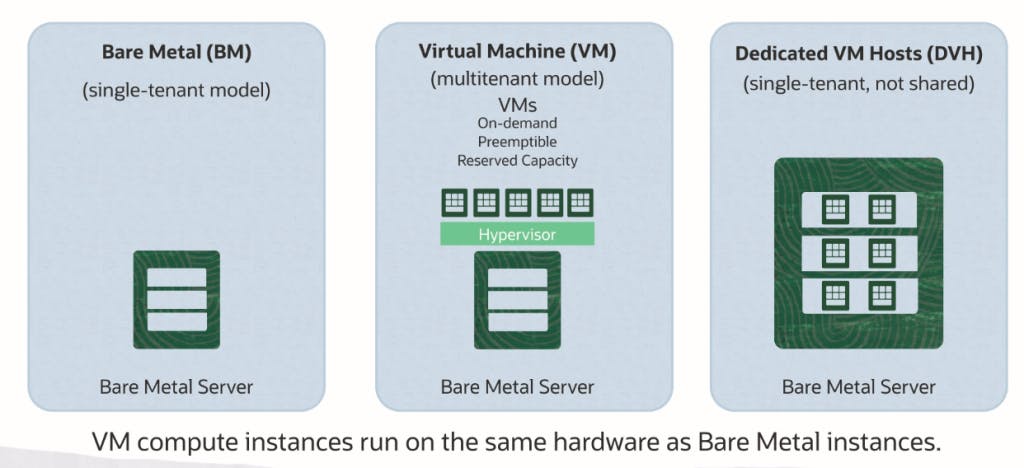
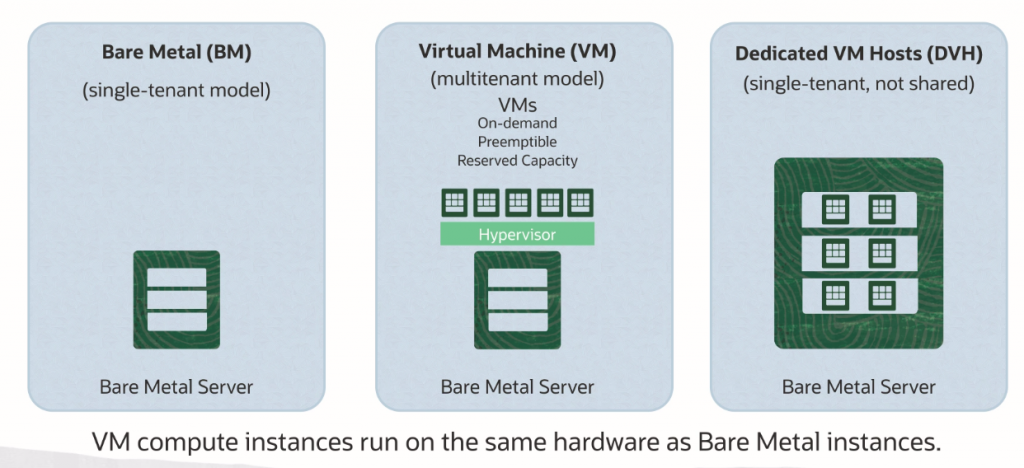
There are two types of instance BM [Bare metal / physical machine], VM[Virtual Machine]
There are two template type
Fixed Shape [BM/VM] : Can not be resized
Flexible Shape [VM only] : Can be resized cpu and memory
Shape Types
Standard Shapes(Designed for general purpose workloads,available with Intel or AMD processors.)
Dense I/O Shapes(Designed for large databases, big data workloads,NVMe-based SSDs)
GPU Shapes(hardware-accelerated workloads,NVIDIA graphics processors)
HPC Shapes(high-performance computing workloads)
Optimized shapes
Standard Shapes : Designed for general purpose workloads and suitable for a wide range of applications and use cases. Standard shapes provide a balance of cores, memory, and network resources. Standard shapes are available with Intel or AMD processors.
Dense I/O Shapes : Designed for large databases, big data workloads, and applications that require high-performance local storage. DenseIO shapes include locally-attached NVMe-based SSDs.
GPU Shapes : Designed for hardware-accelerated workloads. GPU shapes include Intel CPUs and NVIDIA graphics processors.
HPC Shapes : Designed for high-performance computing workloads that require high frequency processor cores and cluster networking for massively parallel HPC workloads.
Optimized shapes
Capacity Type
On-demand capacity
Preemptible capacity
Reserved capacity
Dedicated capacity
You can launch console connections that can be connected from your local machine or cloud itself.
Compute agent provides cpu/memory/io/read/write/network/load metric, which is genrally installed in available images
Default os can also show OS management and top process
Cloud-init script can be setup for executing at provison time
Stop and start does not change the IP [epeheraml ip], however, terminating instance will free that.
Custom Image from computing will only include boot volume, region-specific. Maximum size is 300 GB. Instance will shut down for a few minutes while creating images.
Custom Images can be exported to OS and can be imported
You can move instances in different fault domains but SAME AD
Console connection
Not booting/need to reset ssh key for the OPC user [default user in oracle linux], edit system configuration
Serial console connection / vnc console connection
Need private/public key pair
Stop / start [can choose boot option and can edit boot file]/ reboot logs will display
169.254.0.0/16 These addresses are used for iSCSI connections to the boot and block volumes, instance metadata, and other services.
OS Management Service
To apply patches at operating system provided by OS provider
Support oracle Linux and windows
Yum is mirrored among regions so that patch download does not incur a regional transfer charge
Need to create Dynamic group policy for IAM, allow instances to use OSMS
Install osms-agent service if not installed already
Create Instance group, add instance, and apply the patches on-demand or schedule
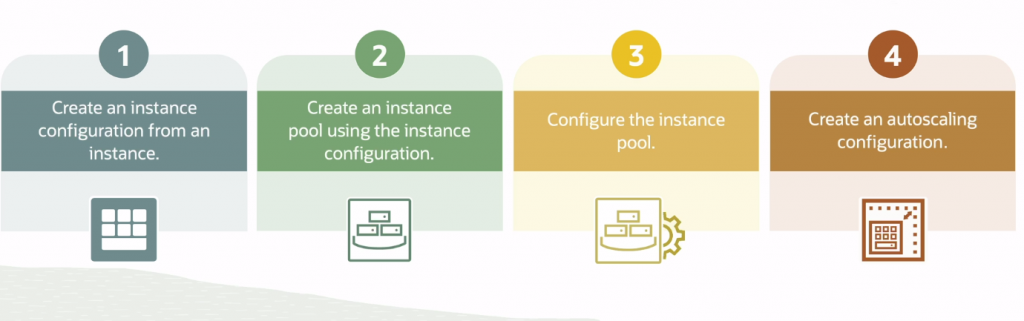
Instance Configuration
- A pre-configuration to launch the instance includes details such as the base image, shape, and metadata.
Instance Pool
Instance pools let you create and manage multiple compute instances within the same region as a group
After you have created an instance pool, you can update the size of the pool, add and remove existing instances from the pool, and attach or detach load balancers
You can automatically adjust the number of instances in an instance pool based on performance metrics or a schedule
When you delete an instance pool, all of its resources are permanently deleted, including associated instances, attached boot volumes, and block volumes
You can use the same instance configuration for multiple instance pools. However, an instance pool can have only one instance configuration associated with it.
ASG [Auto Scaling]:
1-to-1 mapping for ASG and Instance Pool
Scaling is done on the basis of
Metric based
Cpu utilization
Memory utilization
Schedule based: cron expression
Scale pool size
Change in instance state[start or stop]
In Event of Scale-In, instances are terminated first based on how many instances from the instance pool are in that availability domain and fault domain. Within a placement, the oldest instances are terminated first.
Load Balancer
Application Loadbalancer / Network Loadbalancer
Network-based load balancer works on TCP/UDP/ICMP
App-Based load Balancer works on Application Layer [Http/Https]
Load Balancer Public [Comes with Public IP] and Private [With private Ip]
Task: service discovery, health check, Algorithm
Flexible Shape or Dynamic Shape
Layer 4 or Layer 7 LB
You can attach NSG, by default not enabled
LB can be attached to only one subnet
You can enable WAF at LB
Listener : [Same AWS target group]
Weighted round-robin [Round robin with weighted distribution]
Ip Hash [Bound Ip to make a request to the same server]
Least request [Redirect Request to the server which has the least number of conenction]
Up to 16 Listener, 4-state health checks, updated every 3 minute
There can be downtime in change shape as the existing connection will be drained
Health Check status
OK
INVALID_STATUS_CODE
TIMEOUT
REGEX_MISMATCH
IO_ERROR
OFFLINE
UNKNOW
Route based on Virtual Hostname or path-based routing
OCI Traffic Management and Health Checks
- A global Service, generally used in DR/HA to perform Request regional Request Routing
Traffic Management
Policy
Load Balancer [weighted based load balancing]
Failover
Geolocation Steering
ASN Steering
IP Prefix Steering
Health check
Health Check is available for any public ip available [LB, Compute etc]
Check the target from different Vantage points
HTTP based health check or ping type monitors
Performance monitoring from response time
Failover detection
Hybrid Monitoring